Why Is the Atmosphere Important to Earth? What Are the Layers of the Atmosphere?
Earth's atmosphere: Facts about our planet's protective coating

World'due south atmosphere is a sparse band of air made upward of numerous layers based on temperature. Without this protective blanket, life on Globe would not exist equally it protects u.s.a. from heat and radiation emitted from the sun and contains the air we exhale.
Though oxygen is crucial for life on Earth, it is not the master component of our temper. Co-ordinate to education site Vision Learning Globe's atmosphere is equanimous of approximately 78 per centum nitrogen, 21 percent oxygen, 0.93 percent Argon, 0.04 percent carbon dioxide as well as trace amounts of neon, helium, methane, krypton, ozone and hydrogen, too as water vapor.
But only how high does Earth's atmosphere extend? Well that depends on who you enquire! According to NASA the upper layer of Earth's atmosphere — the exosphere — extends up to 6,200 miles (10,000 km), above which the temper and space blend. Though not everyone agrees where infinite actually begins, most scientists concord that the Kármán line, situated 62 miles (100 km) above bounding main level, marks the transition point between Earth and space. Since 99.99997 percent of Earth's atmosphere is located below this signal, information technology'south considered a reasonable height to depict the boundary between Earth and infinite.
Related: What makes World unique?
Globe atmosphere layers
Earth'southward temper consists of 5 main layers from lowest to highest: troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere.
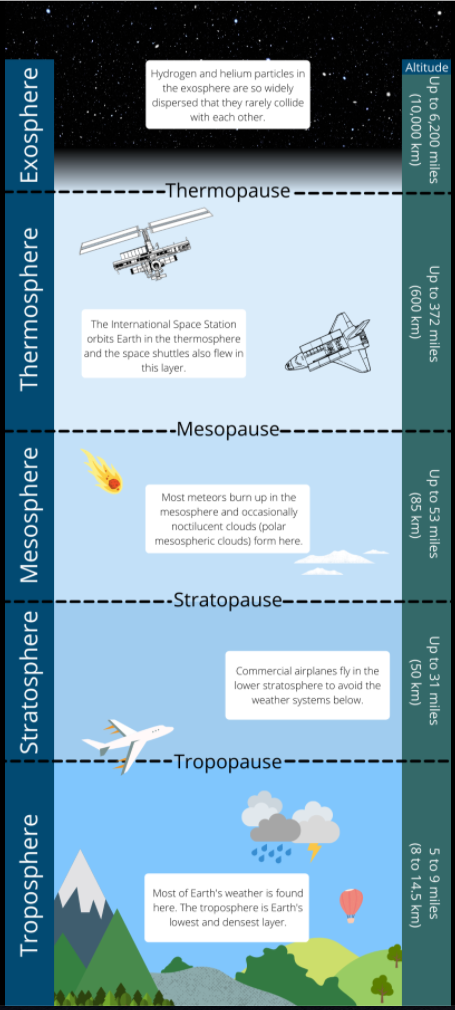
The layers are separated based on temperature according to the National Institute of H2o and Atmospheric Research (NIWA).The atmosphere thins out in each higher layer until the gases dissipate in space. Air force per unit area decreases with altitude. At sea level, air force per unit area is nigh xiv.vii pounds per square inch (ane kilogram per square centimeter), and the atmosphere is relatively dense. At ten,000 feet (iii km), the air force per unit area is ten pounds per foursquare inch (0.7 kg per square cm), which means molecules of gas that make up the atmosphere are less dense. That makes it harder for a person to breathe and become plenty oxygen to live, although there is show for microbial life high up in the clouds.
Troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest and densest layer of the atmosphere and co-ordinate to NIWA, approximately 75% of all the air in the atmosphere is plant in this layer. The troposphere extends from Globe'due south surface to approximately five to nine miles (8 to 14.five km) high.
Did you know?
According to NASA, the acme of the troposphere is lower at World'due south poles and higher at the equator.
According to NASA, "Tropos" means change, and this atmospheric layer lives upwards to its proper noun. Gases are constantly mixing in the troposphere and most of Earth'due south weather is plant here. According to educational website CK-12, turbulence in the troposphere is created when the dominicus warms the Earth's surface, warming the air higher up. The warm air rises and so expands (due to the lower air pressure) and cools. The absurd air sinks forming high pressure systems. According to WorldAtlas nearly helicopters and light airplanes fly in the troposphere.
Stratosphere
The stratosphere is the second layer of World's atmosphere. The stratosphere begins above the troposphere and extends approximately 31 miles (50 km) high. According to NIWA, nearly of the ozone found in Globe's atmosphere is in the stratosphere. Ozone protects us past absorbing harmful UV rays from the sun. The absorption of UV radiation heats upwards the stratosphere and temperatures in this layer actually increase with superlative. Co-ordinate to Weather.gov temperatures in the stratosphere range from approximately -60 degrees Fahrenheit (-51 degrees Celsius) at the bottom to 5 degrees F (-15 degrees C) at the top. Commercial airplanes tend to fly in the lower stratosphere so as to avoid the weather condition systems in the troposphere, co-ordinate to aviation education site Aero Corner.
Mesosphere
The mesosphere is the third layer of Earth's atmosphere. Co-ordinate to NASA the mesosphere begins but above the stratosphere and extends to approximately 53 miles (85 km) high.
The top of the mesosphere, called the mesopause, is the coldest function of Earth's atmosphere, with temperatures averaging virtually minus 130 degrees F (minus 90 degrees C) according to the National Center for Atmospheric Research. The mesosphere is tricky to analyze equally jets and balloons don't get loftier enough but satellites fly as well loftier to directly study the layer. We do however know that almost meteors fire up in this layer, and high-clouds known equally noctilucent clouds (also known as polar mesospheric clouds) occasionally form in the mesosphere.
Thermosphere
The 4th layer of Earth's temper is the thermosphere. It begins just above the mesosphere and extends to approximately 372 miles (600 km) loftier, co-ordinate to NASA. The thermosphere is another atmospheric layer where temperatures rise with distance, according to NIWA. The warming is caused by the absorption of ultraviolet lite and X-rays emitted from the lord's day.
The thermosphere is considered part of World's temper, but air density is so low that nigh of this layer is what is usually thought of as outer space. In fact, this is where the space shuttles flew and where the International Space Station orbits Globe.
Exosphere
The exosphere is the highest layer of Globe's atmosphere and extends from the tiptop of the thermosphere approximately half-dozen,200 miles (10,000 km) above Globe's surface according to NASA. The exosphere is composed of particles of hydrogen and helium, that are then widely dispersed they rarely collide.
Ionosphere
The ionosphere is a very agile layer of Globe'southward atmosphere that spans the mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere, according to NASA. It is not a distinct layer and actually grows and shrinks depending on how much energy it is absorbing from the sun.
We have the ionosphere to give thanks for the beautiful aurora displays that dance across the nighttime sky. Hither, the ions from solar wind collide with atmospheric oxygen and hydrogen molecules, exciting them into higher states of energy. The atoms shed this excess free energy by emitting photons of lite, which we run into every bit the colorful aurora borealis and aurora australis.
What's the difference between conditions and climate?

Broadly speaking atmospheric condition refers to short-term changes in atmospheric conditions whereas climate refers to the boilerplate weather conditions of a specific location over an extended period of time according to the United States Geological Survey. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Assistants (NOAA) further describes the difference simply every bit "climate is what you expect, atmospheric condition is what you get".
Regional climate is defined by the University Corporation for Atmospheric Enquiry every bit the average weather in a place over more than than xxx years. A region's climate is often described, for example, as sunny, windy, dry, or humid. These tin can as well describe the weather in a certain identify, merely while the conditions tin can change in just a few hours, climate changes over a longer span of fourth dimension.
Earth's global climate is an average of regional climates. The global climate has cooled and warmed throughout history. Today, we are seeing unusually rapid warming. The scientific consensus, as stated by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate change (IPCC), is that greenhouse gases, which are increasing because of human activities, are trapping estrus in the atmosphere.
Related: 7 solar system worlds where the atmospheric condition is crazy
Earth, Venus and Mars: Compare the air

To better sympathise the formation and limerick of World, scientists sometimes compare our planet with Venus and Mars. All three of these planets are rocky in nature and are part of the inner solar arrangement, meaning that they are in between the sun and the asteroid chugalug.
Venus' atmosphere is nearly entirely composed of carbon dioxide. The entire planet is shrouded in thick toxic sulfuric acid clouds that trap heat, resulting in what is known as a runaway greenhouse effect. As such, Venus is the hottest planet in the solar system despite being the 2d closest planet to the sun.e. Spacecraft accept to exist heavily reinforced to survive the crushing pressure (xc times heavier than Globe), and the oven-like surface temperatures (900 Fahrenheit or 475 Celsius) hot enough to melt lead, co-ordinate to NASA . s that Venus has no meaning seasonal temperature changes.
Mars' temper is too more often than not composed of carbon dioxide, with traces of nitrogen, argon, oxygen, carbon monoxide and some other gases. The Ruby-red Planet's atmosphere is about 100 times thinner than Earth's — a very unlike situation from the ancient by, when geological evidence shows that Mars used to be much wetter and warmer billions of years ago, co-ordinate to NASA. South. If yous were to stand on Mars and wait to the sky, you'd be greeted with a cherry-red hue caused by dust particles suspended in the air, rather than the blue skies we encounter here on Globe. Due to Mars' thin atmosphere, oestrus from the lord's day rapidly escapes the planet. Co-ordinate to NASA, if y'all stood on the Martian equator at noon, your feet would experience a toasty 75 degrees Fahrenheit (24 degrees Celsius) though temperatures at your head would be rather chilly at around 32 degrees Fahrenheit (0 degrees Celsius).
Scientists routinely compare small, rocky exoplanets to Earth, Venus and Mars to go a better sense of their habitability. The routinely accepted definition of "habitability" is that a planet is close enough to the star for liquid water to exist on its surface. Too far, and the water turns icy; too close, and the water evaporates. Yet, habitability not simply depends on the star-planet distance, merely also the planet's atmosphere, the star'due south variability, and other factors.
Boosted resources
Yous can explore the ionosphere in more item with the National Conditions Service and learn more than about the celebrated increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide from Climate.gov. If you lot fancy reading virtually the fascinating earth of the atmospheric microbiome so bank check out this interesting article in Scientific American.
Join our Infinite Forums to go on talking space on the latest missions, dark sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.
Source: https://www.space.com/17683-earth-atmosphere.html
Post a Comment for "Why Is the Atmosphere Important to Earth? What Are the Layers of the Atmosphere?"